Chartering Plan for Clean Air and Clean Energy
by Smita Mishra December 1, 2021
Earth is known to be the only habitable planet in our Solar system, and so far, only one more Earth- like planet has been identified in our entire galaxy, by scientists. What makes our planet unique is the presence of life supporting factors like air, water and land; but the way we have been exploiting our resources, has caused serious damage to the environment. Irresponsible human behaviour over centuries has pushed Earth into a precarious state where air is polluted, water is contaminated and land is degraded, and if we continue to follow our unsustainable lifestyle, Earth would soon become an inhabitable planet.
People living in the National Capital region in India wouldn’t disagree, as they have been gasping poisonous air every winter, for years. The quality of air in Delhi has been extremely poor, throughout the month of November, this year too.
National Pollution Prevention Day is observed on 2nd December in India. This day is observed in the memory of people who lost their lives in Bhopal gas calamity. Bhopal gas tragedy occurred in the year 1984 on the night of 2–3 December. Many people died due to poisonous gas Methyl Isocyanate also known as MIC that leaked. The idea for celebrating this day is to spread awareness on managing and controlling industrial disasters and the pollution control acts and to prevent the pollution produced by industrial processes or human negligence.
The laws that the nation has for preventing pollution are:
- Water (Prevention and Control of Pollution) Act of 1974
- Water (Prevention and Control of Pollution) Cess Act of 1977
- Air (Prevention and Control of Pollution) Act of 1981
- Environment (Protection) Act of 1986
- Environment (Protection) Rules of 1986
- Manufacture, Storage and Import of Hazardous Chemical Rules of 1989
- Manufacture, Storage, Import, Export & Storage of Hazardous Micro- Organisms Genetically Engineered Organisms or Cells Rules of 1989
- Chemical Accidents (Emergency, Planning, Preparedness and Response) Rules of 1996
- Bio-Medical Waste (Management & Handling) Rules of 1998
- Recycled Plastics Manufacture and Usage Rules of 1999
- Ozone Depleting Substances (Regulation) Rules of 2000
- Noise Pollution (Regulation and Control) Rules of 2000
- Municipal Solid Waste (Management & Handling) Rules of 2000
- Batteries (Management and Handling) Rules of 2001
- Environment Impact Assessment Notification of 2006
- The National Green Tribunal Act, 2010
- Solid Waste Management Rules, 2016
- Hazardous and Other Wastes (Management and Transboundary Movement) Rules, 2016
- Bio-Medical Waste Management Rules, 2016
- Plastic Waste Management Rules, 2016
- E-Waste (Management) Rules, 2016
- Construction and Demolition Waste Management Rules, 2016
The Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB) was constituted in September, 1974 under the Water (Prevention and Control of Pollution) Act, 1974. Further, CPCB was entrusted with the powers and functions under the Air (Prevention and Control of Pollution) Act, 1981. It provides technical guidance to the Ministry of Environment, Forests & Climate Change, Government of India.
While there are different types of pollution in natural resources such as water, air, land or forest – air pollution is probably the most severe one.
Air pollution is responsible for about 2 million deaths in India, and about 7 million deaths, globally, every year. Around 90% people currently breathe air that exceeds the limits for air pollutants, according to WHO guidelines. Apart from affecting human health, air pollution is also responsible for the major challenge being faced by humanity – Climate Change.
Increased carbon content in the air is raising the Earth’s temperature, which in further disturbing the natural balance of Earth’s systems. Melting of glaciers, wildfires and rising sea-levels are signs of catastrophe which can occur anytime in near future. Scientists have been warning of the hazards of air pollution and global warming, and the issue of air pollution, is being addressed by governments of nations across the globe; but the pace and scale of our attempts towards controlling air pollution are not adequate and need immediate strengthening.
Causes of air pollution
For reducing air pollution effectively, it is important first to understand the major causes of air pollution. Though there are some natural phenomena like bio-degradation and wildfires that add pollutants to the atmosphere, but these are minor causes of pollution and do not affect air quality to a great extent. Various human activities like industrial activities, transportation, agricultural activities and poor waste management majorly account for air pollution. Of all these causes, the most significant cause of air pollution is “the burning of fossil fuels”.
Most human activities require energy, for which fuels like coal and petroleum products are burnt, which release toxic gases like carbon monoxide in the atmosphere. Other harmful gases like sulphur dioxide, nitrogen dioxide and particulate matter are released into the atmosphere through industrial and automobile emissions. Reduction of air pollution would be possible, only if we bring changes in the way we carry out various indoor and outdoor activities and minimize the use of fossil fuels.
Air pollution control
Governments of nations across the globe have been formulating laws to control air pollution which have been able to reduce pollution to some extent, but it is the duty of every individual to follow measures to reduce pollution effectively.
Government laws for reducing air pollution
Steps taken by government of India to control air pollution include:
- Compulsory PUC (pollution under control) certificate of petrol driven vehicles which test for carbon monoxide and hydrocarbon
- Permission to use only pure diesel with a maximum of 500 PPM Sulphur as fuel for vehicles
- Use of non-polluting compressed natural gas CNG only as fuel by buses and trucks
- Compulsory mixing of 20% ethyl alcohol with petrol and 20% biodiesel with diesel
These need to be adhered to, by industries in true spirit, in order to control emissions.
Steps to reduce air pollution:
- Avoid use of vehicles wherever possible
- Use public transportation
- Use electric vehicles and bicycles
- Use energy responsibly
Role of business in reducing air pollution
Air pollution is a major concern for business community too. Companies have been considering air pollution control for their Corporate Social Responsibility activities, but it is also important for them to ensure pollution control throughout their supply chains. Here are some steps that can be followed by companies to reduce air pollution:
- Calculate carbon foot-print and offset carbon emissions
- Choose raw materials responsibly
- Check air pollution throughout the supply chain
- Use renewable energy
UN SDGs for controlling air pollution
The UN SDGs are committed to reduce air pollution and its effects in many ways. some SDG targets are directly related to air pollution control and some others support it.
 |
SDG 3.9: substantially reduce the number of deaths and illnesses from hazardous chemicals and air, water and soil pollution and contamination by 2030 |
 |
SDG 2: improving soil quality |
 |
SDG 7: clean energy |
 |
SDG 9.4: clean technologies and industrial processes |
 |
SDG 11: Sustainable cities and communities |
 |
SDG 12: Responsible consumption and production |
World Energy Conservation Day (December 14, 2021)
National Energy Conservation Day is observed every year on December 14. The day focuses on making people aware of global warming and climate change and promotes efforts towards saving energy resources. Essentially, the main objective of the day is to reduce the use of energy and to encourage people to use it efficiently.
Renewable energy
Growing awareness of the hazards of burning fossil fuels, have led to rising demand of renewable energy. There are abundant resources present in nature, that are capable of generating clean energy, some of which are being used already and some are to be explored.
India is one of the leading nations, in terms of producing energy from renewable sources. India’s present installed electricity generation capacity from renewable sources is 136GW (as of 27 November 2020, which is 38% of its total installed electricity generation capacity (373 GW), and is much ahead of meeting its committed target of achieving 40% of its electricity generation from fossil fuels by 2030, in the Paris Agreement. In fact, India aims for achieving 57% of its total electricity capacity from renewable sources, by 2030.
Major renewable energy sources in India and their capacities.
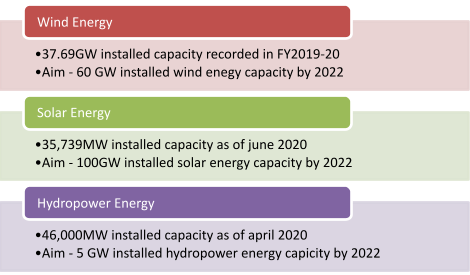
Apart from these major renewable energy sources, India is looking forward to adopt new ideas for generating power from renewable sources, for fulfilling its ever rising demand of energy, while conserving nature.
There is also an urgent need to generate employment and business opportunities to help our economy recover the damage caused due to the global pandemic, through innovations. Both these demands could be met by coming up with economically viable projects for producing renewable energy. Scientists all around the world are involved in research and development programmes in renewable energy sector, for supporting both the environment, and the economy.
Generating energy from Industrial waste
Waste management is a major concern for all industries. So far, people have been working on providing safe and eco-friendly solutions for disposal of industrial waste, but in recent years, people have come up with innovative ideas for managing waste in a productive and profitable way. Generating electricity from industrial waste is an emerging trend and many institutions are already involved in research and development programmes for facilitating the same. As per studies, industrial waste can be used to generate power, in all its forms; solid waste, waste water and waste gases.
.png)
Biogas power plant
Biogas has been widely accepted in India as a household fuel, especially in rural areas. it is majorly used for cooking, but it is now being considered as a fuel for generating electricity. Bio gas power plants are based on the process of biodegradation of cow dung and other bio-waste, and are therefore highly cost-efficient and eco-friendly.
Recently, Haryana’s first grid-connected 1.2 MW bio-gas based power plant has been commissioned. Such plants are well supported by government policies and would prove to be a promising business plan in near future.
Geothermal energy
Geothermal power plants are popular renewable energy establishments in USA and many European countries. These plants make use of the heat that comes from the sub surface of Earth, to generate electricity. Deep wells are dug to access the hot water present under rocks and use it to drive turbines.
Many sites in India are being tested for geothermal energy, and the country’s first geothermal power plant has been set up in Gujarat’s Dholera, where immense heat was found under the Earth in the form of hot springs. The plant would produce 20 KW of electricity. India has the potential to produce much higher amount of electricity through geothermal power plants, and add to its economic development
Tidal energy
The tides of Seas and Oceans carry tremendous energy; this energy can be harnessed and converted into electricity by installing power generation set-up at suitable sites. Presently, there are very few tidal power plants around the world, but tidal power has the potential to become a major source of renewable energy
Marine algae as biofuel
Studies are being conducted all around the world, to derive techniques for commercial use of Marine algae as biofuel. The potential of marine algae is well known to scientist and researchers working on biofuel sources. Marine algae are considered superior to terrestrial plants in terms of storing solar energy and carbon. They also have higher photosynthetic efficiency and higher biomass yield. Marine algae are expected to play an important role as biofuel for producing energy in future.
Business opportunities in air pollution control
Many entrepreneurs are coming up with innovative products to reduce air pollution, some of which have already gained popularity and some would become popular eventually. Government policies support such businesses and investors too are willing to invest in responsible business plans.
Products and business ideas that support air pollution control
- Electric vehicles
- Solar panels
- Air purifiers
- Portable gardens
- Green roofs
- Nature positive building materials
Green energy entrepreneur
Various types of power plants for producing electricity are definitely large-scale projects. But this does not mean, green energy is not meant for small entrepreneurs. Entrepreneurs too have great prospects in implementing green energy solutions at small scale. There are various products and services associated with generation, storage, conservation and distribution of energy, providing innumerable innovative business opportunities for entrepreneurs. Through research, training and planning, anybody can become a green energy entrepreneur or a green energy investor, and contribute to the Nation’s sustainable development.
PREVIOUS POST
Advent of 5G, Adjacent Innovation and Opportunities (for Start-Ups)NEXT POST
Paving the way for customer satisfactionLatest Update
-

An Ethic of Responsibility
01-11-2021



